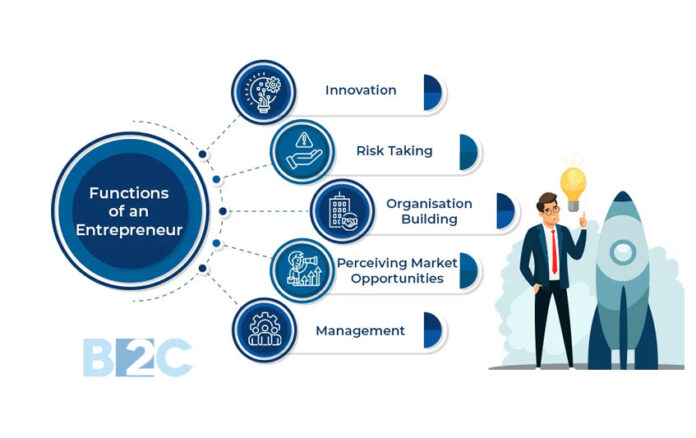
Starting and operating a small business requires an entrepreneur to wear many hats and juggle multiple responsibilities. From developing business strategies to managing finances, marketing, and employees, entrepreneurs have a lot on their plates. Understanding the key duties and obligations is crucial for the success and growth of any small business. This article explores the diverse responsibilities entrepreneurs take on when running a small business.
Entrepreneurship involves recognizing opportunities, taking risks, and launching new ventures. An entrepreneur assembles the necessary resources and manages all aspects of a business. Entrepreneurs come up with business ideas, convert them into business ventures, and assume responsibility for their development.
Small businesses are independently owned firms that have fewer employees and less annual revenue compared to larger enterprises. The definition of “small” varies by industry and region. Small businesses make up over 90% of all firms in the US and create around 60-80% of new jobs annually. They play a vital role in driving innovation, economic growth, and prosperity.
For small businesses, the entrepreneur usually handles all core functions personally, especially in the early stages. Understanding the diverse duties and obligations involved in running a small business is critical for entrepreneurs to succeed. This article will explore these key responsibilities that entrepreneurs must manage as small business owners and managers.
Key Responsibilities of Entrepreneurs in Small Businesses
Running a small business entails many crucial responsibilities for the founding entrepreneur. Here are some of the main duties entrepreneurs handle in small business management:
Creating a Business Plan and Strategy
One of the first steps entrepreneurs take when starting a small business is crafting a business plan. This document articulates the company’s objectives, structure, operations model, target market, competitive advantage, and financial projections.
A solid business plan is indispensable for accessing funding, recruiting talent, and launching the venture. It also helps create a strategy to guide the business. Entrepreneurs must regularly review and adapt strategies based on internal capabilities and external market factors.
Managing Finances and Accounting
Most small business owners oversee finances and accounting to control cash flow and costs. Key responsibilities include:
- Maintaining financial records
- Tracking income and expenses
- Managing accounts receivable/payable
- Preparing financial statements
- Managing payroll
- Filing taxes
- Controlling inventory
- Budgeting and forecasting
Proper financial management and accounting procedures are vital for small business success.
Handling Legal and Compliance Responsibilities
Small business owners must comply with diverse legal and regulatory requirements that apply to their sector, location, and operations. This includes business registration, permits, insurance, taxes, health and safety regulations, employment laws, sector-specific regulations, and more.
Entrepreneurs must identify and fulfill all compliance obligations to avoid penalties. Working with legal counsel can help navigate regulations. Proper legal protections for intellectual property and contracts are also the entrepreneur’s responsibility.
Managing Marketing and Sales
Marketing is essential for customer acquisition and revenue generation. Small business owners usually directly oversee marketing activities like market research, branding, advertising, digital marketing, public relations, tradeshow participation, and sales initiatives.
They develop marketing budgets and plans tailored to the target audience and business goals. Tracking performance metrics helps refine strategies. Strong marketing enables small businesses to compete with larger players.
Ensuring Outstanding Customer Service
Delighting customers through stellar service quality helps earn loyalty and referrals. Entrepreneurs set customer service standards and train staff to consistently deliver positive experiences.
Small business owners might personally handle customer queries and complaints to nurture relationships. Investing in customer satisfaction drives growth for small businesses.
Identifying Hiring and HR Needs
As small businesses grow, entrepreneurs must determine hiring needs and find suitable employees. Recruitment, screening, selection, onboarding, training, performance reviews, and general HR duties become the entrepreneur’s responsibility.
They must ensure HR management adheres to labor regulations. Small companies often outsource certain HR functions, but entrepreneurs oversee HR strategy. Managing people is a top priority.
Overseeing the Team
Entrepreneurs in small startups usually directly manage their team on a day-to-day basis. They oversee workflows, assign tasks, monitor progress, provide feedback, and ensure collaboration.
As organizations expand, founders hire managers for different areas but still guide operations at a broader level. Effective team leadership is vital for small business success.
Managing Day-to-Day Operations
From inventory control to customer service, technical issues to supplier relationships, small business owners are deeply involved in daily activities. Entrepreneurs make decisions on operations and processes to deliver products/services efficiently.
Staying agile, responding quickly to challenges, and continuously improving operations are key operational responsibilities. Smooth operations allow small businesses to execute plans and fulfill customer needs.
These are the primary areas of responsibility that need entrepreneurs’ attention in small business management. Wearing multiple hats and learning to balance diverse duties are par for the course when starting and growing a small enterprise.
Financial Management for Small Businesses
Meticulous financial management is imperative for small businesses to thrive and steer clear of cash flow issues or debt traps. Entrepreneurs must make financial decisions judiciously by adopting best practices:
Importance of Financial Management for Small Businesses
- Essential for profitability and sustainability
- Helps make data-driven decisions
- Enables strategic allocation of resources
- Allows tracking of progress versus financial projections
- Helps manage cash flow smoothly
- Crucial for securing funding for growth
Robust financial control provides small businesses with a firm fiscal foundation.
Tips for Managing Small Business Finances
Here are some tips for entrepreneurs to effectively manage finances:
- Monitor cash flow daily and weekly with budgeting tools
- Use accounting software to create invoices, track income/expenses, and generate reports
- Follow standard accounting procedures for recording transactions
- Leverage digital tools for efficient invoicing, payments, payroll etc.
- Manage receivables diligently to ensure timely customer payments
- Take advantage of small business tax deductions and credits
- Build an emergency reserve fund to handle unexpected costs
- Compare financial KPIs against projections and adjust strategies if required
- Seek professional accounting assistance for complex compliance needs
Automating and streamlining financial processes enables entrepreneurs to stay on top of their finances.
Understanding Financial Statements and Accounting Principles
Knowing how to interpret key financial statements is vital for small business owners. The three main reports are:
Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity on a set date. It helps assess the business’s net worth.
Income Statement: Summarizes revenues, expenses, and profit/loss over a period. It shows the company’s operating performance.
Cash Flow Statement: Shows inflows and outflows of cash. It helps understand changes in cash balances.
These statements should be prepared using standard accounting principles like GAAP or IFRS. Entrepreneurs must understand accounting fundamentals to make smart financial decisions.
Seeking Professional Help for Financial Management
While entrepreneurs handle day-to-day finances, complex tasks like payroll, taxes, audits, and accounting systems are best managed by financial professionals. Small businesses should have an accountant and work closely with bankers.
Outsourced CFO services are also available to handle core financial functions. This allows entrepreneurs to focus on business growth.
With sound financial management discipline, small businesses can optimize profitability and cash flow. Tracking KPIs and getting professional support enables prudent fiscal oversight.
Marketing Strategies for Small Businesses
Marketing is the lifeline of any small business. Entrepreneurs need to master strategic marketing to attract customers and compete successfully.
Importance of Marketing for Small Businesses
- Creates brand awareness
- Helps acquire and retain customers
- Drives revenue and cash flows
- Builds competitive advantage
- Enables communication with target audience
- Allows tracking of marketing ROI
- Helps understand customer needs and wants
- Essential for growth
Without solid marketing, small businesses cannot thrive. Owners have to continually invest time and money in impactful marketing.
Key Marketing Strategies for Small Businesses
Here are some of the most effective marketing approaches for small businesses:
Define target audience: Identifying niche target segments allows tailored messaging. Buyer personas help refine strategies.
Build a strong brand: Logo, tagline, messaging, visual identity, and overall branding needs consistency. Be recognizable.
Create a well-designed website: Websites are sales hubs providing 24/7 visibility. Good SEO drives traffic. Include lead capture forms.
Leverage social media marketing: Post engaging content consistently on relevant platforms. Social ads also help reach targets.
Run targeted online ads: PPC, display ads, retargeting help generate leads. Track conversions.
Email marketing: Building an email list enables regular communication with subscribers via newsletters, promotions etc.
Produce helpful content: Blog posts, videos, guides establish the brand as an industry thought leader.
Network and referrals: Attend events, and conferences and build word-of-mouth through referrals. Low-cost strategies.
Monitor and optimize: Use Google Analytics to track website traffic. Run A/B tests on ads and content. Pivot strategies based on data.
Blending traditional and digital marketing with clear goals and budgets boosts small business success.
Building a Brand and Identifying Target Audience
Entrepreneurs need to craft a strong brand identity and persona. Defining the target audience is crucial too.
Brand Identity: Logo, colors, name, messaging, tone, and visuals should be aligned and consistent across platforms. This generates recognition.
Target Audience: Identify niche audience segments like demographics, interests, values, and behaviors. Create detailed buyer personas.
With a memorable brand and deep understanding of customers, small business marketing gains traction.
Creating a Website and Using SEO
A functional website is indispensable for small businesses today. SEO boosts site visibility:
Website essentials: Simple navigation, responsive design, contact forms, testimonials, calls-to-action. Update regularly.
Optimize for SEO: Include target keywords in content. Improve site speed and mobile-friendliness. Produce fresh blog posts regularly.
Websites are the digital flagships of modern small businesses. Leveraging SEO helps attract more organic traffic.
Social Media Marketing and Advertising
Social platforms present excellent marketing opportunities for small businesses:
Business pages on relevant platforms: Showcase brand, products, content, offers. Post regularly to nurture followers.
Engaging content: Share visual content, behind-the-scenes, thought leadership posts to build community.
Paid ads: Geo-targeted social media ads help reach local audiences. Retargeting keeps brand top-of-mind.
Influencer marketing: Partnerships with relevant influencers expose brands to new audiences.
Social media enables direct, real-time communication with customers at relatively low cost.
Networking and Building Relationships
In-person and digital networking still play a big role:
- Attend trade shows, conventions and networking events to connect with prospects
- Join industry associations and local chambers of commerce
- Build relationships with local media contacts
- Collaborate with complementary brands
- Gain referrals through word-of-mouth
Networking helps raise brand visibility and get more personal in front of potential customers.
With the right strategies and tools, small business owners can drive growth through marketing. Tracking results and quickly adapting to changes in competitive and consumer landscapes is vital. This keeps marketing efforts agile and effective.
Human Resource Management for Small Businesses
Managing people is crucial, regardless of company size. Entrepreneurs in small businesses have to master certain HR responsibilities.
Importance of Human Resource Management for Small Businesses
- Helps find and hire suitable talent as per strategic needs
- Enables new employee onboarding and training
- Manages employee expectations and enhances engagement
- Boosts productivity through performance management
- Ensures legal and regulatory compliance
- Builds positive and collaborative work culture
- Allows open communication and feedback
Even with few employees, proper HR practices create an environment for teams to thrive and grow.
Key Responsibilities of Entrepreneurs in HR Management
Small business owners themselves manage core HR activities:
Workforce planning: Project hiring needs, skill gaps based on goals and anticipated growth. Plan recruitment.
Recruiting: Source candidates through job portals, social media, referrals. Screen applicants.
Interviewing and selection: Assess candidate fit through structured interviews. Extend job offers.
Onboarding: Orient new hires on culture, processes through onboarding programs.
Training and development: Conduct onboarding training. Manage ongoing learning through L&D programs.
Performance management: Set individual goals, provide regular feedback, conduct reviews.
Workplace safety and culture: Ensure a positive, collaborative, and safe work environment.
Compliance: Adhere to employment laws and regulations. Avoid lawsuits.
HR might be outsourced partially as the company grows. But entrepreneurs continue providing strategic direction.
Hiring and Recruitment Strategies
Hiring the right people is critical. Smart recruiting enables this:
- Identify skills and cultural fit needed for open positions
- Post vacancies on niche job boards, LinkedIn, social media
- Offer competitive pay and employee perks in job posts
- Screen resumes and select qualified applicants to interview
- Ask situational and behavioral interview questions
- Check references to validate candidate background
- Extend job offer to the selected finalist
Well-defined hiring processes help attract and onboard suitable talent.
Employee Training and Development
Investing in people boosts performance:
- Conduct thorough onboarding training on culture, systems, and processes
- Roll out regular skills training workshops related to roles
- Support participation in external training programs, conferences
- Encourage people to expand skills through online courses
- Offer tuition reimbursement for advanced education
- Provide cross-training to gain experience in diverse functions
- Develop high-potential employees for leadership roles
A learning culture empowers teams and elevates small businesses.
Performance Management and Evaluation
Measuring employee performance enables growth. Effective techniques:
- Set clear goals, objectives, and metrics for each role
- Establish weekly check-ins and regular one-on-one meetings
- Seek feedback from peers, managers, customers
- Conduct annual or bi-annual reviews to discuss progress
- Provide recognition for achievements
- Address performance issues promptly through training or discipline
- Benchmark salaries and bonuses against industry data
Continuous feedback loops keep people aligned with organizational goals.
With lean yet skilled teams, small businesses can deliver outstanding products and services. Strategic HR practices allow entrepreneurs to motivate and retain top talent.
Planning and Strategy for Small Businesses
Careful planning and adaptable strategies provide startups and small companies essential direction for growth and resilience.
Importance of Planning and Strategy for Small Businesses
- Gives roadmap and focus to achieve goals
- Allows tracking of progress versus projections
- Focuses resource allocation as per strategic priorities
- Helps prepare for future risks and opportunities
- Enables data-driven decision making
- Provides benchmarks to measure performance
- Ensures business continuity if key people leave
- Positions small business competitively
Planning and strategy enable ambitious entrepreneurs to build enterprises that last.
Developing a Business Plan and Setting Goals
Crafting a solid business plan is the first step:
Elements of business plan
- Executive summary
- Business description and history
- Products/services offered
- Market analysis and competitive assessment
- Target audience and buyer personas
- Marketing and sales strategies
- Management team
- Operations plan
- Financial projections
Goal-setting
- Vision statement
- 12-month and 3-year goals
- Financial projections
- Hiring objectives
- Growth forecasts
- Product/service development pipeline
The business plan provides actionable strategic direction to accomplish goals. Track progress through KPIs.
Adapting to Market Trends and Changes
Markets evolve constantly. Agility and adaptation are key:
- Continuously monitor industry news, competitor moves, and consumer trends
- Modify products and services to align with market changes
- Refine pricing to stay competitive
- Leverage emerging technologies to improve processes, offerings
- Pursue new opportunities and partnerships
- Adapt marketing messaging and formats to resonate with audiences
- Exit activities that are no longer productive
Staying reactive to external forces allows small businesses to remain relevant.
Identifying Growth Opportunities and Risks
Looking ahead helps identify potential growth levers and risks:
Growth opportunities
- Expanding to new markets or locations
- New customer segments to target
- Product or service line extensions
- Strategic partnerships and collaborations
- Improving operations efficiency
- New marketing and sales channels
Risks to mitigate
- Competitors launching better products
- Loss of key staff
- Rising costs eroding margins
- Negative market or economy shifts
- Supply chain disruptions
- Changing regulations and compliance landscape
By recognizing both opportunities and risks early, strategic decisions become easier.
Creating a Contingency Plan
A contingency plan enables continuity if faced with disasters:
- Document procedures to ensure operations can continue if key systems fail
- Keep critical inventory buffer stock to handle supply chain disruptions
- Cross-train employees and document processes to prepare for loss of key staff
- Arrange lines of credit or emergency funding to overcome sudden cash crunches
- Have business interruption and loss insurance to cushion against financial hits
- Develop crisis communications plan for reputation management
With strategic agility and contingency plans, small businesses gain resilience to navigate uncertainties and thrive long-term.
Legal and Compliance Responsibilities for Small Businesses
Navigating legal obligations and regulations is a crucial entrepreneurial responsibility to avoid issues down the line.
Importance of Legal and Compliance Responsibilities for Small Businesses
Meeting legal and compliance requirements is necessary for:
- Operating legitimately with proper business licenses, permits, insurance
- Paying local, state and federal business taxes
- Following industry regulations and standards
- Protecting intellectual property like trademarks, copyrights, and patents
- Safeguarding customer and employee data to avoid privacy breaches
- Maintaining accurate financial records and reporting as per accounting standards
- Adhering to labor regulations around hiring, compensation, workplace policies
- Implementing mandated health and safety measures
- Ensuring products/services comply with legal standards
- Avoiding lawsuits, penalties, fines, and criminal charges
Regulatory adherence allows small businesses to focus on growth with peace of mind. Neglecting compliance puts companies at risk.
Understanding Business Laws and Regulations
Entrepreneurs must understand laws and regulations influencing their venture:
Business entity structure: Decide between LLC, S-Corp, C-Corp, Partnership etc. based on liability, taxes.
Intellectual property: Trademark brand name and logos. Copyright materials. Patent products and inventions.
Employment and labor: Comply with laws on hiring, wages, discrimination, harassment, safety etc.
Industry regulations: Follow all rules and codes of conduct governing your sector.
Privacy and data security: Protect customer and employee personal data. Follow protocols.
Licenses, permits, insurance: Acquire all documentation needed for legal operations.
Taxes: Pay income taxes, payroll taxes, sales tax, and local taxes consistently.
Contracts: Use agreements to protect dealings with vendors, partners, staff.
Stay updated on all laws affecting business activities, facilities, products, and people.
Protecting Intellectual Property and Data
Safeguarding intellectual property and private data is imperative:
- Register trademarks, copyrights, patents with government IP offices
- Include non-disclosure agreements in employee and contractor contracts
- Install data security software and controls to prevent breaches
- Limit internal access to confidential data on a need-to-know basis
- Craft clear data use policies for staff
- Follow protocols for collecting, storing, sharing consumer data
- Continuously monitor data systems for intrusions
Vigilance helps secure critical IP and data. Lax protection can lead to loss of competitive advantage or lawsuits.
Ensuring Workplace Safety and Health
Providing a hazard-free workplace is a legal necessity:
- Comply with all occupational health and safety regulations
- Install guards on dangerous equipment and safety signage
- Provide personal protective equipment like gloves, masks, glasses
- Train staff on safe work practices and emergency response protocols
- Report accidents, injuries, near-misses
- Conduct fire safety drills and first aid/CPR training
- Monitor facilities for risks and fix identified hazards
Worker health should never be compromised for profits. A culture of safety boosts small business success.
Managing Risk and Liability
Balance prudent risk management with growth:
- Transfer risks by taking adequate business insurance coverage
- Include liability disclaimers, warranties, and limits in customer contracts
- Separate business and personal assets for liability protection
- Consult experts like lawyers to review high-risk processes, products
- Conduct due diligence on partners, vendors, and contractors
- Document internal policies, procedures and compliance checklists
- Build emergency reserves and contingency funds
With proactive risk assessment and mitigation, small businesses secure their future.
By staying legally compliant, documenting policies, securing data and IP, and embracing a culture of safety and ethics, entrepreneurs can avoid issues that lead to business disruption. This enables sustainable growth.
Conclusion
Running a small business necessitates wearing many hats and managing diverse responsibilities – from strategic planning to financial oversight, marketing to talent management, and regulatory compliance. Performing these roles successfully allows entrepreneurs to turn their ambitions into thriving enterprises.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the key obligations entrepreneurs take on when starting and operating small companies. Understanding core duties such as crafting business plans, managing finances prudently, executing marketing strategies, hiring and managing people, and complying with laws and regulations provides a foundation for growth.
Beyond checking the boxes on essential business functions, successful entrepreneurs also cultivate skills like adaptability, resilience, market awareness, and passion for their vision. By balancing duties with strategic thinking and growth-focused leadership, small business owners can build companies primed for longevity and innovation.
The responsibilities are undoubtedly challenging but also highly rewarding, as entrepreneurs get to convert their dreams into realities while creating economic value and employment. Those who embrace the diverse roles with diligence and patience are best positioned to evolve their enterprises from humble startups into influential industry players. So take the leap, be prepared to hustle and learn every step of the way, and the entrepreneurial journey can bear fruitful outcomes.